
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide, but a diagnosis doesn't have to be a life-altering setback. With the right knowledge, a proactive approach, and a strong partnership with your healthcare provider, you can effectively manage the condition and lead a full, healthy life. This guide will walk you through the essential steps of diagnosis and provide practical strategies for control.
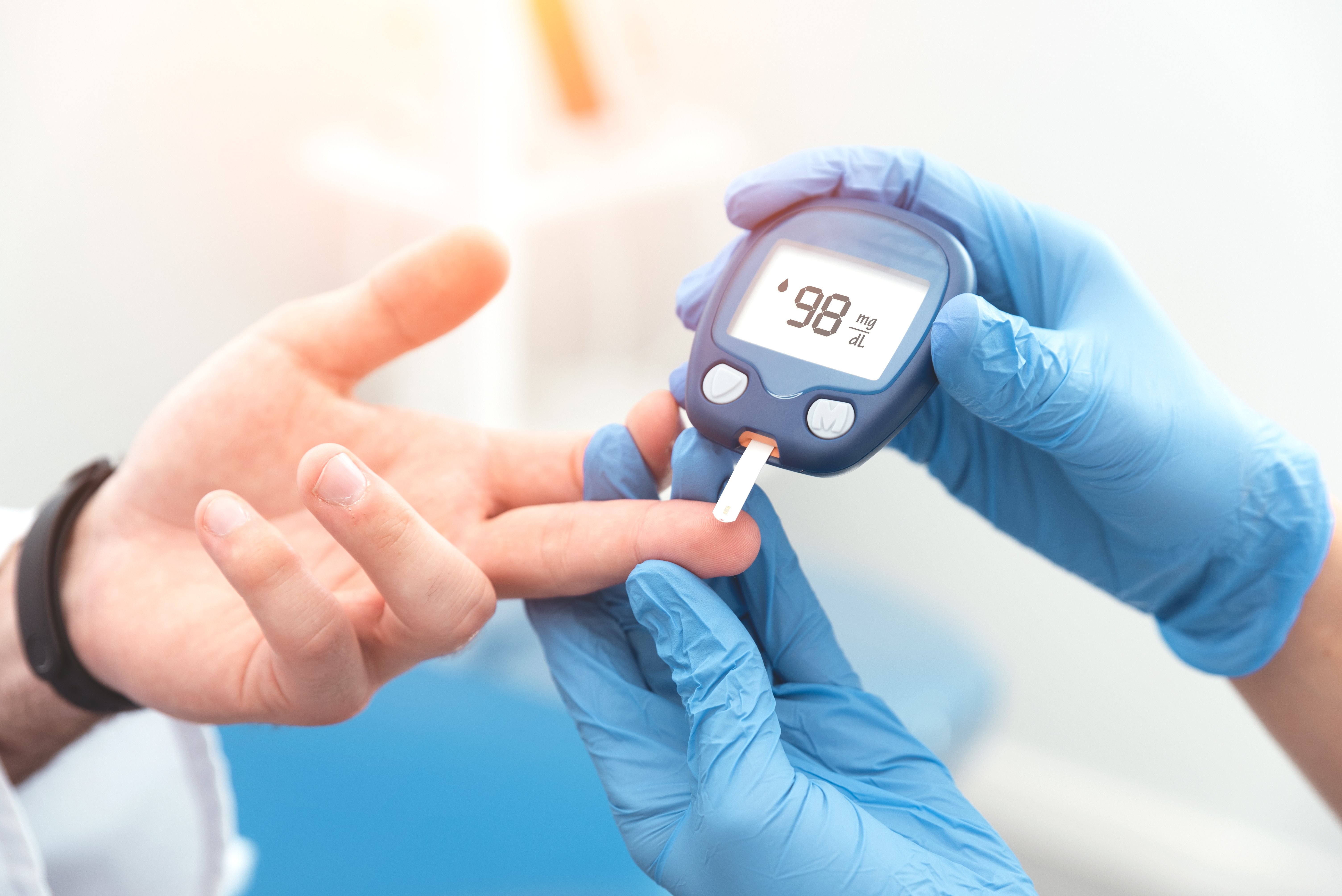
Often, the early signs of diabetes can be subtle or even non-existent. That's why regular check-ups and a simple blood test are so crucial. Here's a look at the common diagnostic tests:
While a blood test is the definitive way to diagnose diabetes, be aware of potential symptoms, especially if they are persistent:
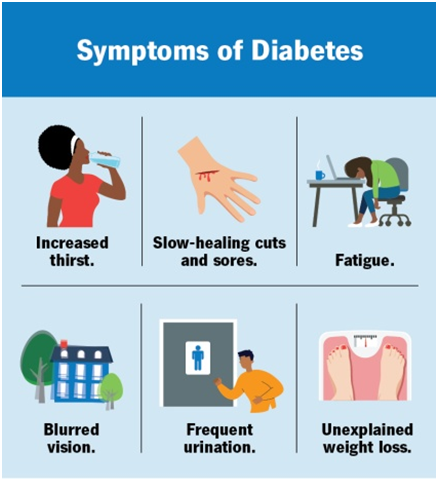
If you experience any of these, it’s a good idea to talk to your doctor and get tested.
A diabetes diagnosis isn't a dead end—it's a call to action. The good news is that with dedicated management, you can prevent or delay complications and feel your best. The cornerstones of diabetes control are lifestyle modifications and, if necessary, medication.
Partnering with Your Doctor For many people, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough. This is where modern medicine comes in.
- Oral Medications: There are various pills that can help your body produce more insulin, use insulin more effectively, or slow down glucose absorption. Metformin and glimepiride may help to control blood sugar, however its recomended to consult your doctor before taking it. Some of ready brands with composition of Metformin and glimepiride are GLIMIKO-GP1, GLIMIKO-1G, GLIMIKO-MK-GP1A diagnosis of diabetes is not the end of a healthy life—it’s the beginning of a new, more informed approach to wellness. By understanding the diagnostic process and embracing a proactive plan that includes a healthy diet, regular exercise, and consistent communication with your healthcare provider, you can not only manage diabetes but also thrive. Take it one step at a time, celebrate your successes, and remember that you are in control.
Content in this blog has taken from various offline and online sources and for information purpose only, so please consult your doctor before taking any medicine and its adivse to avoid self medication.

A newcomer to the world of Pharma Manufacturing, focused on mastering GMP standards and contributing to quality through meticulous execution.
Name
DateComment